What are Petechiae?
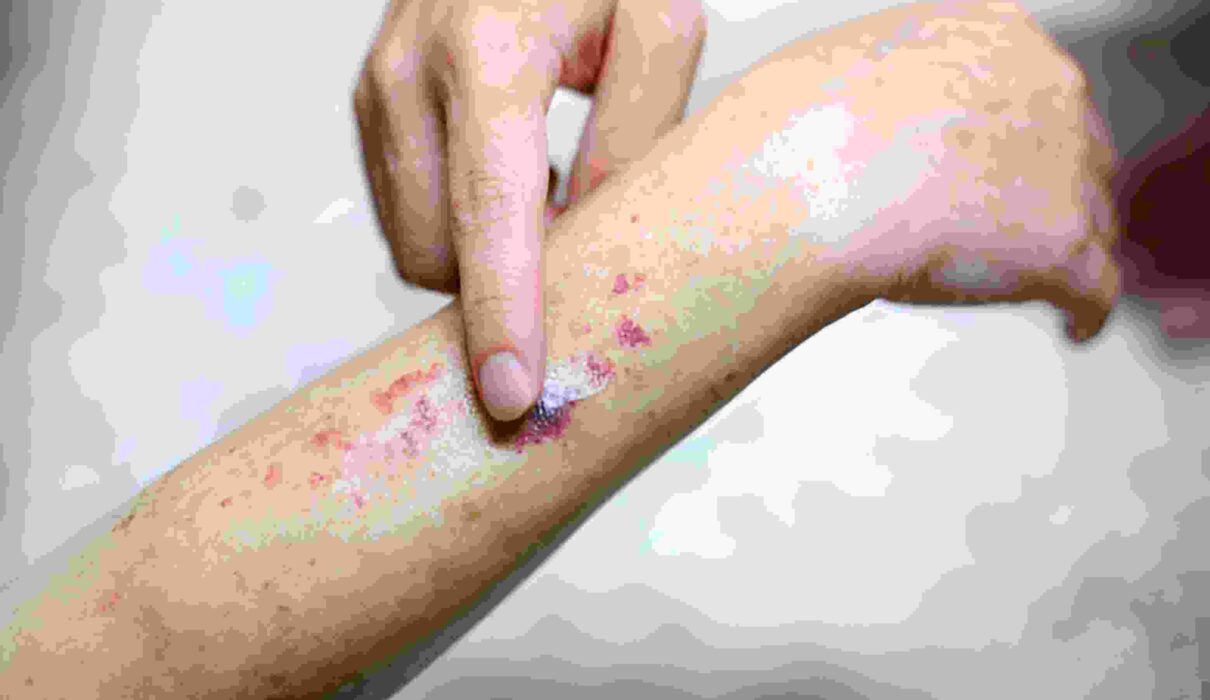
Petechiae are tiny red, brown, or purple spots on the skin when minor blood vessels break and leak blood into the skin layers. These spots typically measure 1-2 millimeters in diameter and don’t fade when pressure is applied. Unlike more extensive bruises, petechiae appear as clusters of tiny dots, giving the skin a distinctive speckled appearance.
Common Locations
Petechiae frequently appear in specific areas of the body. The most common locations include the lower legs, ankles, and feet, where blood pressure is highest due to gravity. They can also appear on the arms, face, inside the mouth, and eyelids. In children, petechiae often appear on the neck and chest area, particularly after severe coughing or vomiting episodes.
Visual Characteristics
When examining petechiae pictures, several key features help distinguish them from other skin conditions. The spots appear flat against the skin, unlike raised rashes or hives. They often cluster together in patches but maintain distinct boundaries between individual spots. The color can vary depending on how recently the bleeding occurred, with newer petechiae appearing bright red and older ones taking on a brownish or purple hue.
Causes and Associated Appearances
Different underlying conditions can create distinctive patterns of petechiae. For instance:
- Thrombocytopenia-related petechiae typically appear suddenly and widespread across the body
- Trauma-induced petechiae often concentrate in specific areas where pressure or injury occurred
- Infectious causes may show petechiae accompanied by other symptoms like fever or general rash
- Sun damage can lead to chronic petechiae in exposed areas, particularly in older adults
- Medication-related petechiae might appear symmetrically across the body
Diagnostic Value
Medical professionals use petechiae pictures for several purposes. They help document the progression of various conditions, assist in differential diagnosis, and monitor treatment effectiveness. The pattern, distribution, and accompanying symptoms visible in these images provide valuable diagnostic clues. For example, rapidly spreading petechiae might indicate a severe blood disorder, while localized patches might suggest minor trauma.
Documentation and Monitoring
Specific techniques help capture their appearance effectively when photographing petechiae for medical documentation. Using good lighting, including a size reference in the image, and taking pictures from multiple angles provide comprehensive documentation. Sequential photographs can track changes over time, helping healthcare providers assess whether conducts are working or worsening the condition.
Differentiating Features
Pictures help distinguish petechiae from similar-appearing conditions:
- Unlike purpura, petechiae are smaller and more numerous
- While cherry angiomas are also red, they appear raised and dome-shaped
- Heat rashes typically cause small bumps rather than flat spots
- Flea bites usually have a central puncture point
- Regular bruises are more significant and may change color differently over time
Warning Signs in Images
Specific visual characteristics in petechiae pictures may indicate more serious conditions requiring immediate medical attention. These include:
- Rapidly spreading petechiae
- Petechiae accompanied by large areas of skin discoloration
- Symmetrical patterns appear suddenly across multiple body areas
- Petechiae around the eyes or in mucous membranes
- Dense clusters that appear to be merging into larger patches
Understanding how to interpret petechiae through images helps healthcare providers and patients recognize when these small spots might indicate a minor issue versus a more serious condition, demanding prompt medical evaluation. Regular photographic documentation can provide valuable information about the progression of underlying conditions and the effectiveness of treatments.