Visual Characteristics
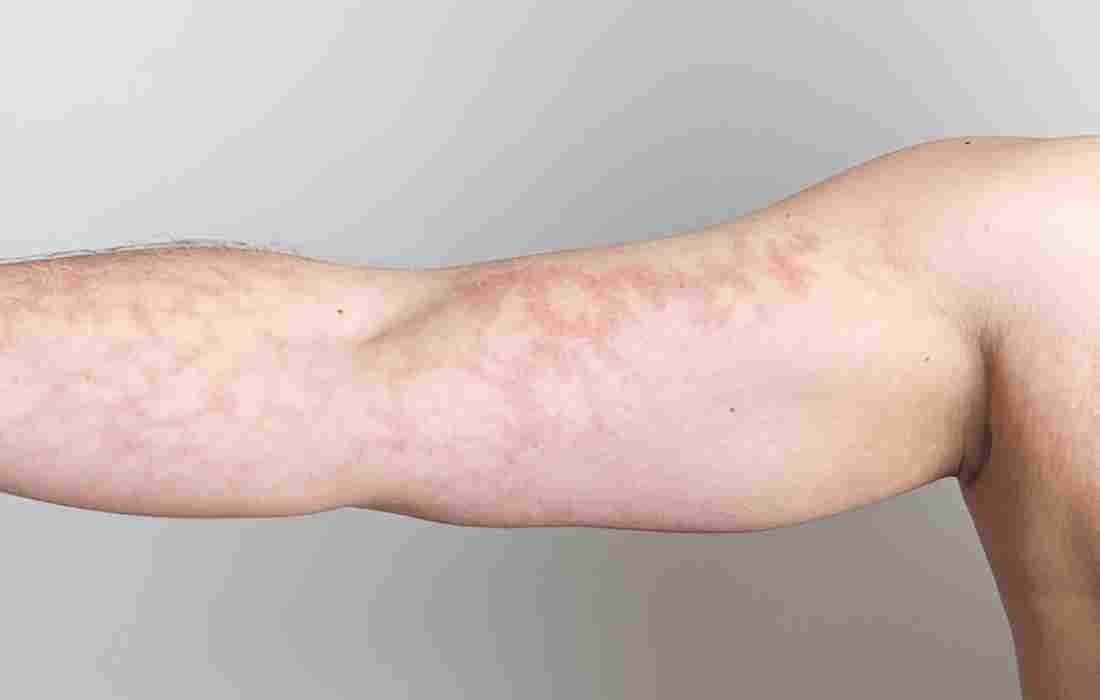
Mottled skin presents as a patchy pattern of discoloration, where areas of the skin appear to have irregular spots or patches of different colors. This often manifests as a marbled appearance with alternating light and dark areas in photographs. The patterns can range from subtle variations in skin tone to more pronounced patches that may appear purple, red, or bluish.
Photographic Documentation
Medical photography of mottled skin requires careful attention to lighting and exposure settings. Proper documentation typically includes images taken under consistent, diffused lighting to capture the pattern’s subtleties accurately. Close-up shots help reveal the intricate network of discolored patches, while wider shots show the overall distribution across affected areas.
Common Presentation Areas
Photos frequently focus on areas where mottling commonly appears, such as the legs, arms, and torso. The pattern may be more pronounced in extremities, particularly in conditions affecting circulation. Images often show how the mottling can become more visible when the affected area is exposed to temperature changes or when positioned below heart level.
Clinical Significance
Medical photographs of mottled skin serve several essential purposes in healthcare:
- They provide baseline documentation for tracking changes over time
- They assist in diagnostic processes by allowing comparison with known patterns
- They facilitate communication between healthcare providers
- They help monitor treatment effectiveness
- They serve as educational tools for medical training
Differential Patterns
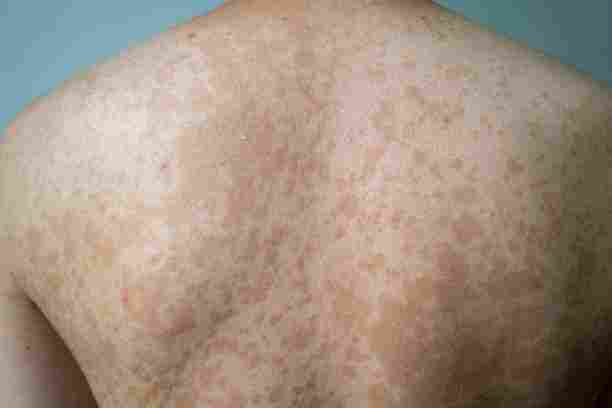
Photographic documentation helps distinguish between different types of mottling. Some patterns appear as acceptable, lace-like networks (livedo reticularis), while others may show more significant, more irregular patches (livedo racemosa). The photographs can reveal subtle differences in color, pattern distribution, and border characteristics that aid in differential diagnosis.
Technological Considerations
Modern digital photography has enhanced our ability to document mottled skin through:
- High-resolution sensors that capture fine detail
- Standardized color calibration for accurate representation
- Cross-polarized lighting techniques to reduce glare
- Digital image analysis tools for pattern recognition
- Secure storage systems for maintaining patient records
Temporal Changes
Sequential photography is crucial in monitoring how mottled skin patterns change over time. Images may show variations in:
- Pattern intensity throughout the day
- Response to environmental factors
- Progression or improvement with treatment
- Development of new areas of involvement
- Changes in color or distribution
Understanding mottled skin through photography requires attention to detail and standardized documentation methods. These images provide valuable information for clinical practice and research, helping healthcare providers better understand and treat the underlying conditions that cause skin mottling. The photographic record is an objective measure of the condition’s progression and response to treatment, making it an indispensable tool in dermatological and vascular medicine.